Slack is a powerful collaboration tool, but security becomes a top priority when sensitive data is involved. For organizations bound by regulations like PCI DSS and HIPAA, using Slack securely requires extra vigilance.
Following best practices, you can leverage Slack’s power while keeping your organization’s sensitive data safe and secure.
Why security matters on Slack
Even the most user-friendly platforms require robust security measures to protect sensitive data and maintain business continuity.
Slack has become a communication hub for many organizations, but its ease of use can’t overshadow the crucial fact that security is paramount. A single lapse can have devastating consequences, as evidenced by the infamous 2022 Uber hack. In this incident, a hacker infiltrated Uber’s systems through a seemingly simple method: social engineering via Slack. The attacker impersonated an IT worker and tricked an employee into revealing their login credentials. This one compromised login became the key that unlocked Uber’s internal systems, exposing sensitive data and causing significant disruption.
Slack security can’t be an afterthought. Here’s why:
- Slack connects many people within an organization. This creates a larger potential target pool for attackers than traditional, siloed communication methods.
- Data sharing. It can include sensitive data depending on the organization. A compromised account becomes a gateway to this sensitive information.
- Many organizations allow guest access for collaboration. Guest accounts can be exploited without proper controls to gain a foothold within the system.
Essential Slack security settings and features
PLEASE NOTE: some futures are available only for Enterprise Grade Security at Slack.
Two-factor authentication (2FA)
Setup 2FA for your Workspace:
- Sign in to the appropriate workspace, and visit your Account page at my.slack.com/account/settings.
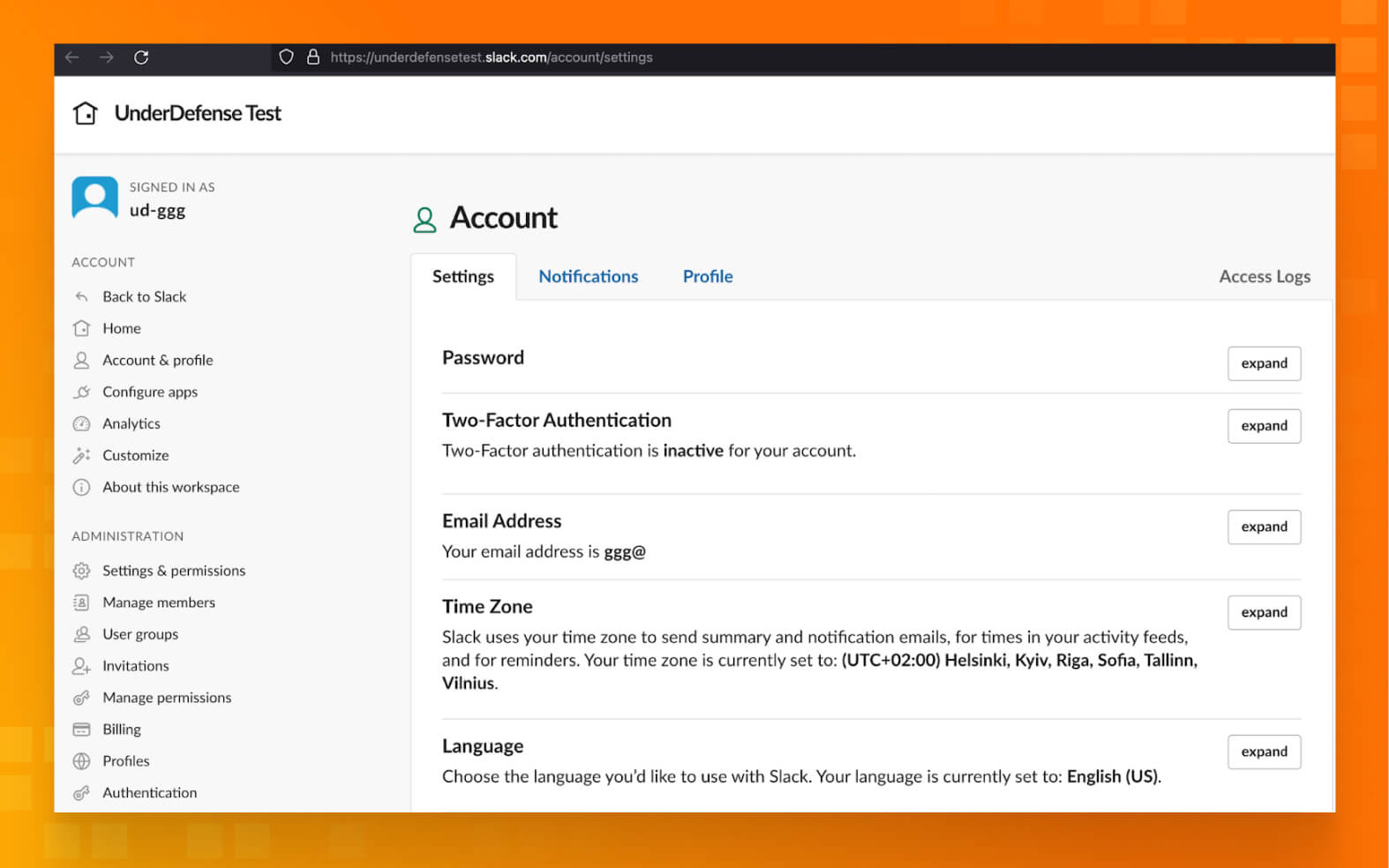
Next to Two-factor Authentication, click Expand. Then, click Set Up Two-Factor Authentication.
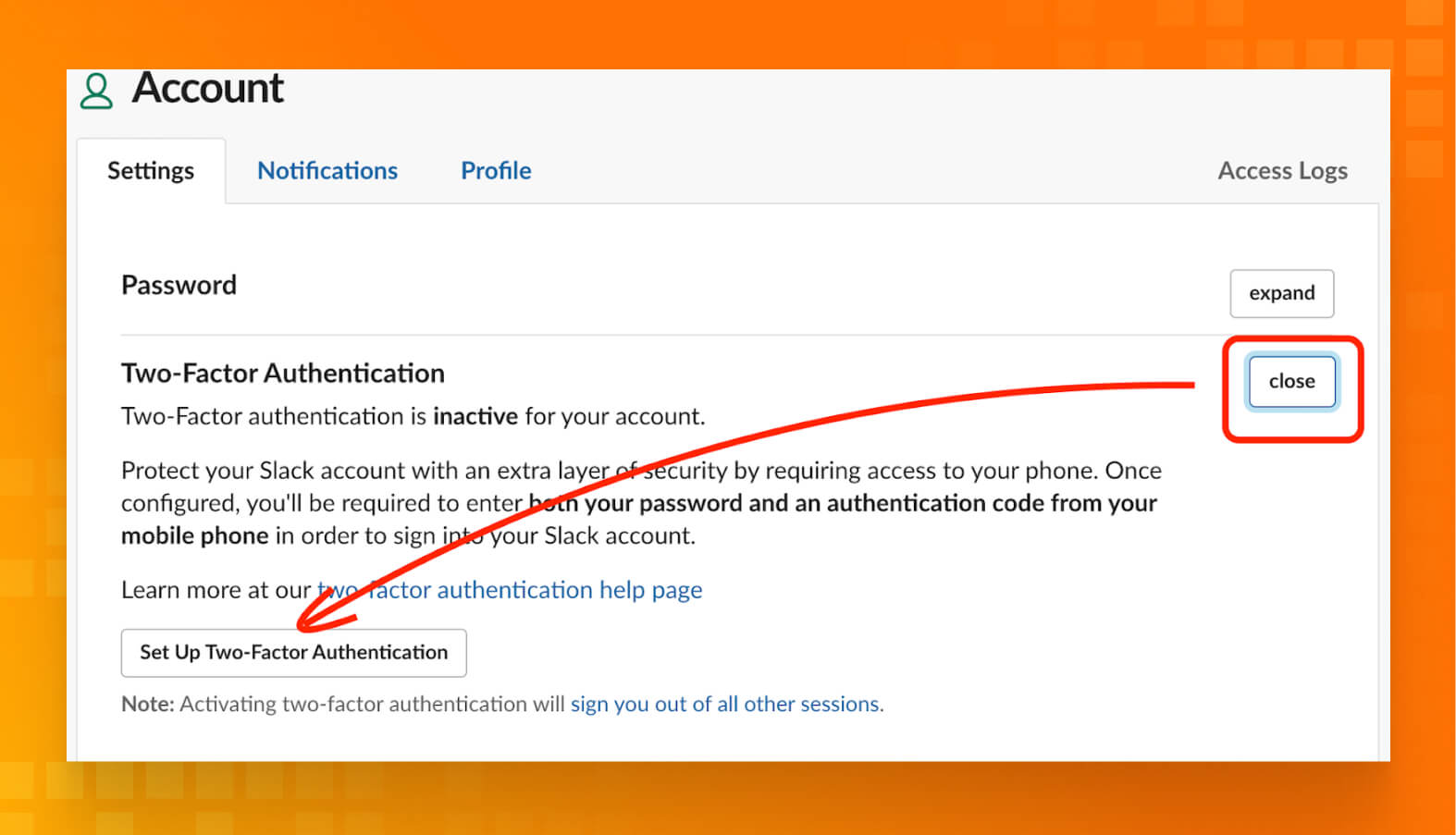
- Enter your password, and click Use an app to retrieve authentication codes from the authentication app on your device.
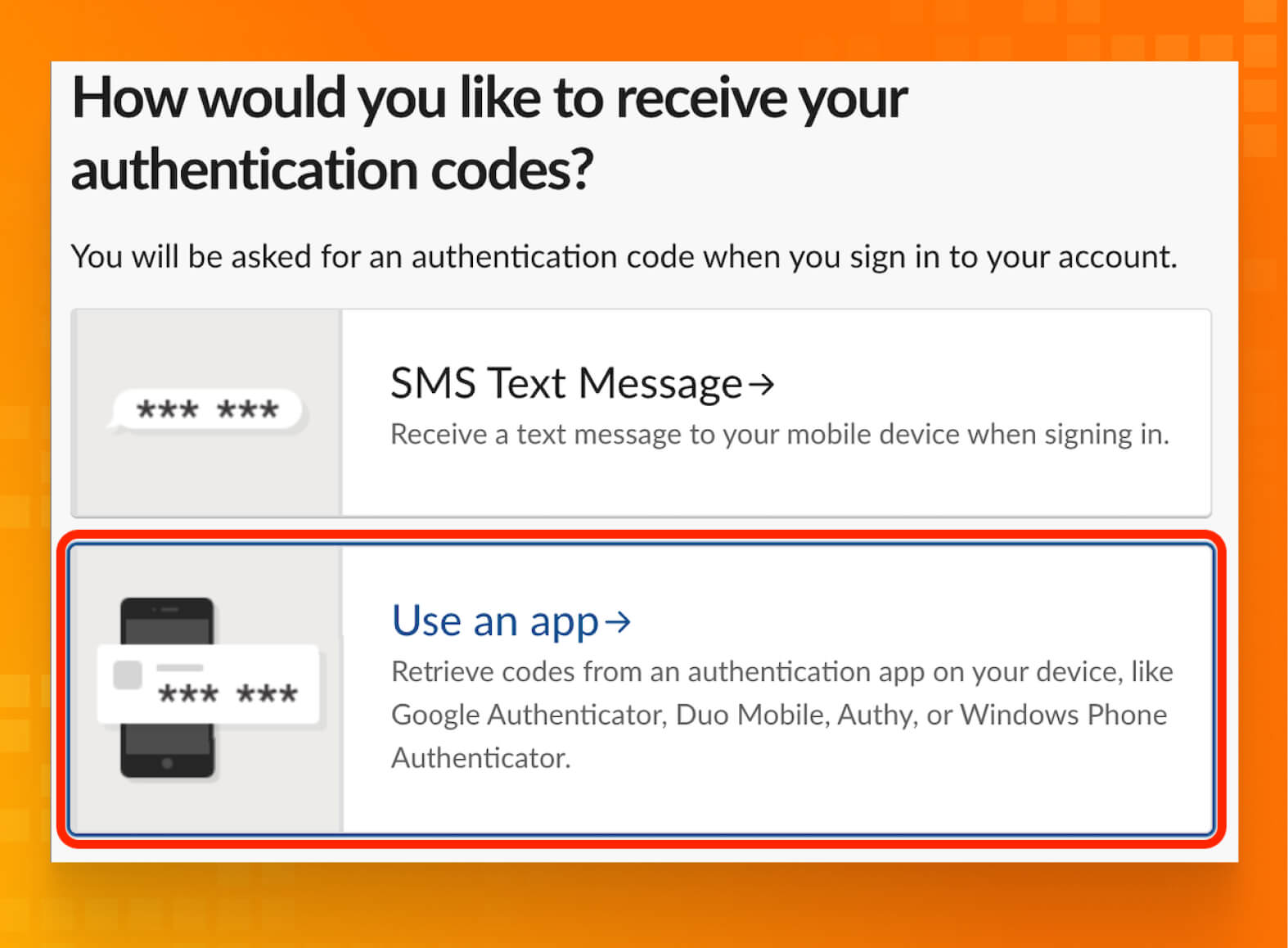
- Add a new account. In most apps, you can do this by tapping the + icon.
- Scan the QR code using your device’s camera. Alternatively, you can enter the code by hand.
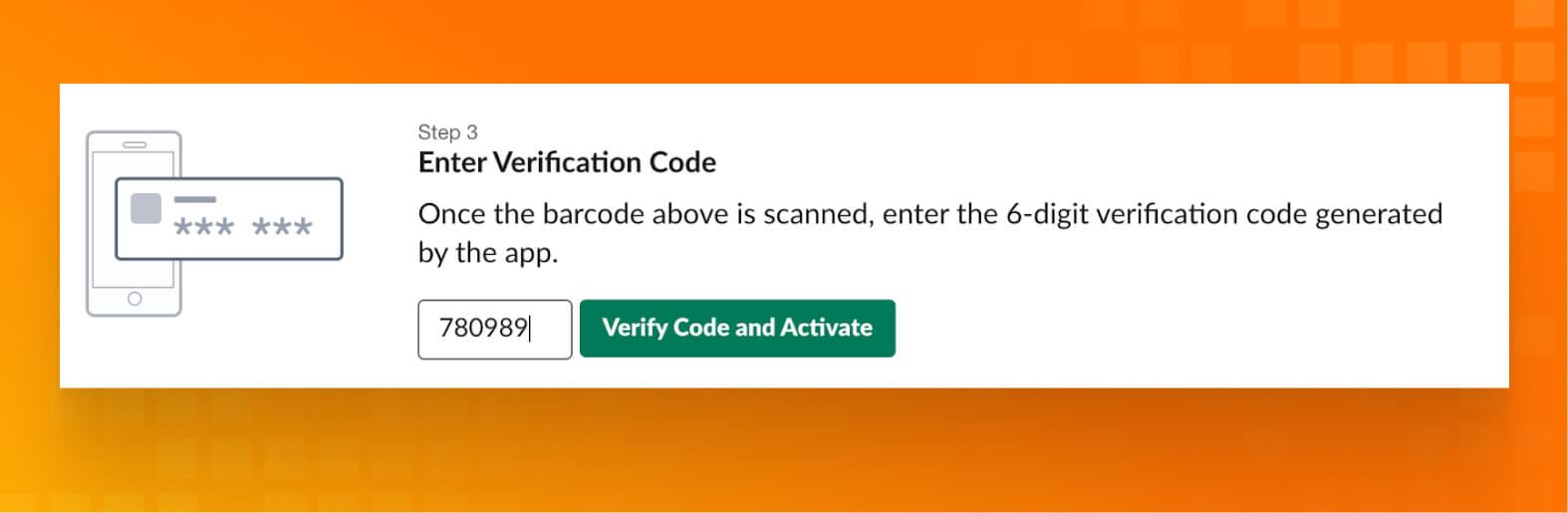
- On Slack’s 2FA configuration page, enter the 6-digit verification code that your authentication app generates.
- To finish, press Verify Code.
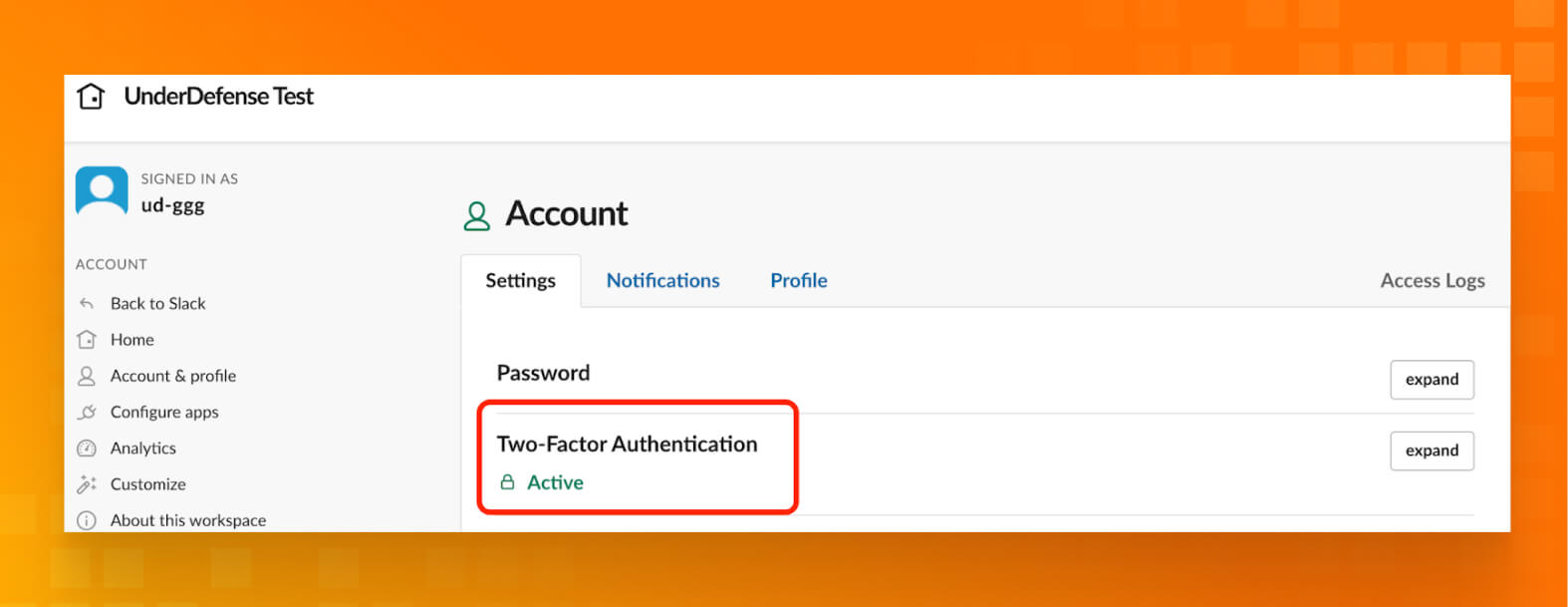
- Finally, we have 2FA status “ACTIVE.”
Turn on mandatory 2FA
- Click Authentication.
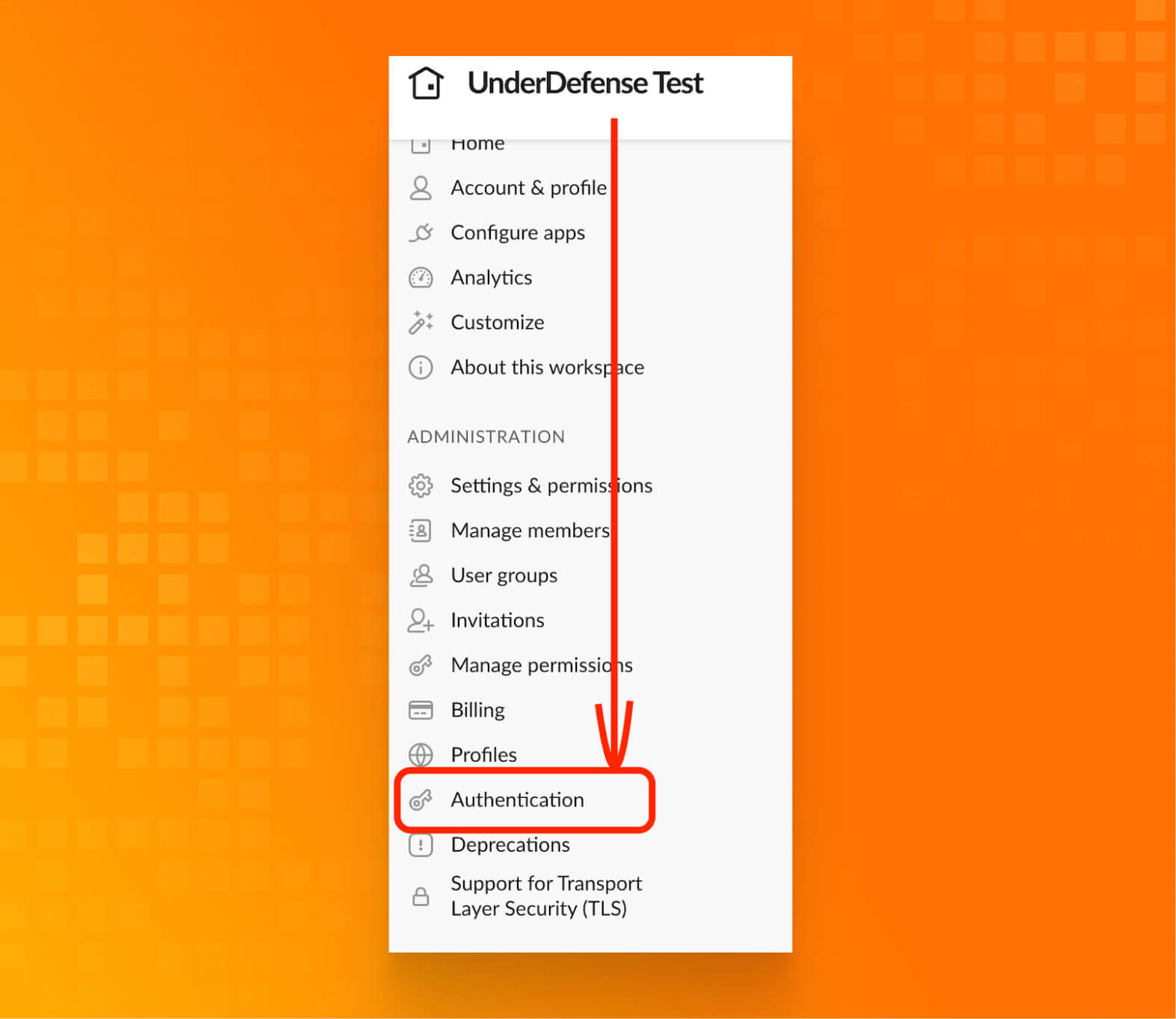
- Next to Two-factor authentication for your workspace (2FA), click Expand.
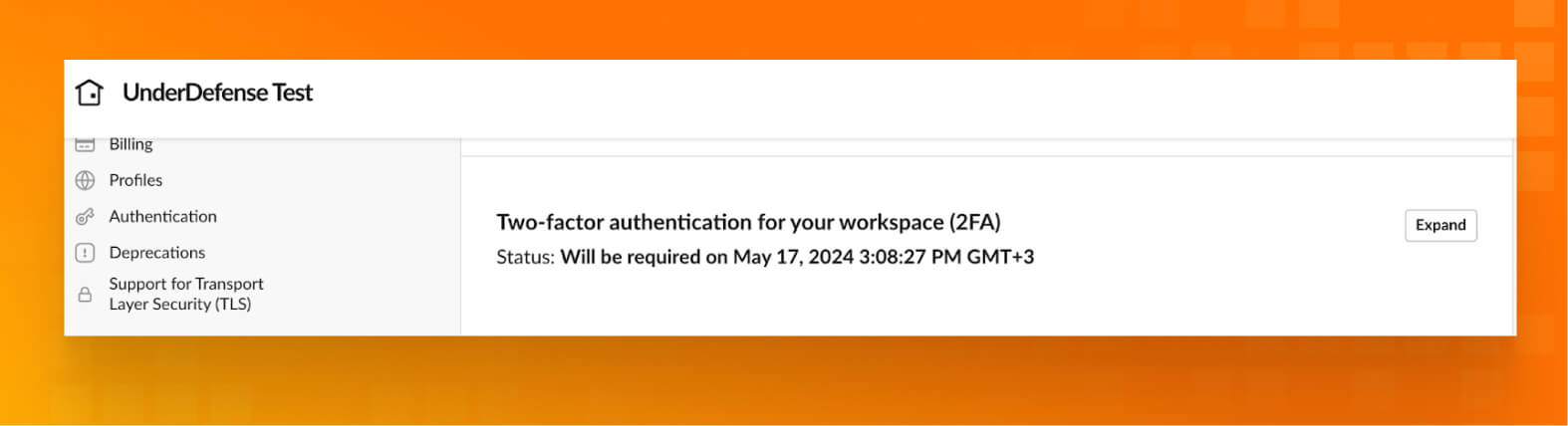
- Click Enable 2FA for your workspace. If you’d like, click Require an authenticator app to prevent people from using SMS for 2FA.
- Click Activate two-factor authentication. Members will get an email and Slackbot message to help them set up.
- The status of 2FA will be changed to “Will be required on __.”
URL Source:
https://slack.com/help/articles/204509068-Set-up-two-factor-authentication
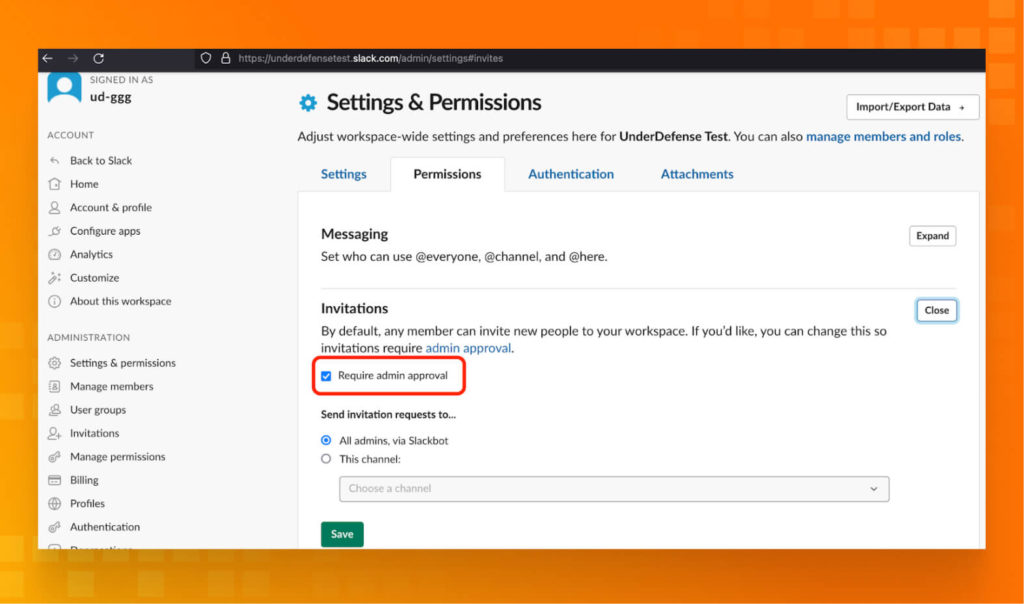
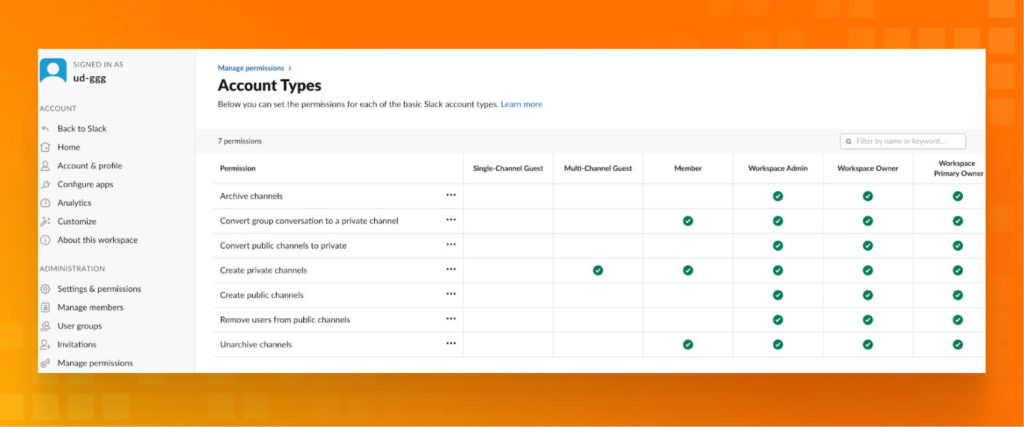
User role management
https://underdefensetest.slack.com/admin/permissions/account-types
Validate Permission Sets to be sure that you are following the rule of the MINIMUM rights.
URL Source:
https://slack.com/help/articles/1500004132581-Assign-members-to-system-roles#business+-plan-1
Data encryption
Slack encrypts data at rest and in transit by default, ensuring your data is secure while stored on Slack’s servers and during transmission between your devices and Slack.
Enterprise Key Management (EKM) is an additional security measure you can consider, depending on your plan and needs.
For the highest level of control (available with Enterprise Grid), you can manage your encryption keys through AWS Key Management Service (KMS). This provides more granular control over data access and encryption.
URL Source:
https://slack.com/resources/slack-for-admins/slack-enterprise-key-management-implementation-guide
Best practices for secure communications on Slack
Secure channels
- Channel access control:
- Restrict who can create channels to prevent unnecessary clutter and potential security risks. Consider an approval process for new channels.
- Assign membership to channels based on “the least privilege” principle (Role Based Access Control)
- Use private channels for sensitive discussions and keep public channels for general communication.
- Data handling within channels:
- Limit guest access, especially in private channels containing sensitive information.
- Use integrating Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools to monitor for sensitive data leaks within channels. DLP can help prevent accidental or malicious data sharing.
- Implement clear and descriptive channel names that don’t contain sensitive information. Avoid using names that could be a target for attackers.
- Additional security measures:
- Enforce a review process for channel invitations to prevent unauthorized access.
- Establish a policy for archiving or deleting inactive channels to minimize data storage and potential security risks.
How to handle sensitive information
- Ask yourself, “Does this information absolutely need to be on Slack?” Consider alternative, more secure communication channels for highly sensitive data.
- Choose private channels with limited membership based on “the least privilege” principle. Public channels are not suitable for sensitive information.
- Use temporary file-sharing options for sensitive documents. Set expiration dates to automatically delete the files after a designated timeframe.
- Strictly limit guest access, especially in channels containing sensitive information. Guests should not have the ability to view or download sensitive data.
- Use DLP integration to protect your sensitive data.
Phishing awareness
Slack’s ease of communication can make it a target for phishing attacks. Here’s how to cultivate a culture of awareness and protect your organization from these malicious attempts:
- Educate your users:
- Conduct regular phishing simulations within your Slack workspace. These controlled exercises help users identify red flags.
- Develop and distribute quick reference guides summarizing key phishing indicators for easy access within Slack. These can be pinned to relevant channels or incorporated as slash commands for on-demand reference.
- Promote a culture of caution:
- Encourage users to report any suspicious links or messages encountered within Slack. Create a designated channel or reporting mechanism for easy communication of potential threats.
- Promote a culture of verification before clicking on links or downloading attachments. Train users to hover over links to preview the destination URL and confirm senders before engaging with messages.
Integrations and Third-Party Apps
Integrations and third-party apps can greatly enhance Slack’s functionality and introduce potential security risks. Here are some best practices for managing integrations and third-party apps securely:
- Thoroughly vet third-party apps: Check the app’s reviews, ratings, and security-related feedback. Look for any known security issues or breaches associated with the app. Prefer apps from reputable providers with a strong track record of security.
- Limit app permissions: Only grant the necessary permissions that the app requires to function. Avoid giving apps access to sensitive data if it’s not necessary. Regularly review the scopes and permissions requested by the app and ensure they align with your security policies.
- Use approved integrations: Search Slack’s App Directory for integrations that Slack has vetted for security and compliance. Implement a custom approval process for new integrations to ensure they meet your organization’s security standards.
- Regularly audit integrations: Conduct regular audits of all third-party apps and integrations to ensure they are still necessary and secure. Disable or remove integrations no longer in use to reduce potential attack vectors.
- Monitor activity and access: Enable and monitor third-party app activity logs to detect unusual or unauthorized activities. Set up alerts for any significant changes or suspicious activities involving third-party apps.
- Data handling and privacy: Ensure third-party apps comply with your data handling and privacy policies. Verify how they store, process, and protect your data. Prefer apps that use encryption for data both in transit and at rest.
- Restrict integration installation: Limit who can install third-party apps and integrations. Typically, only admins or a specific team should have this capability. Educate users on the risks associated with third-party apps and encourage them to seek approval before installing any new integrations.
- Use enterprise solutions: If available, use solutions that offer enhanced security and management features for third-party apps. Utilize Slack’s Enterprise Key Management to have greater control over encryption keys used by third-party apps.
- Security policies and compliance: Ensure third-party apps comply with industry standards and regulations relevant to your business, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or SOC 2. Conduct security assessments and require vendors to provide evidence of their security practices and certifications.
- Incident response for third-party apps: Have a clear incident response plan for dealing with security breaches or issues arising from third-party apps. Maintain open lines of communication with third-party vendors to quickly address any security concerns or breaches.
Regular audits and compliance
- Regular audits:
- Schedule periodic audits, typically quarterly or semi-annually, to review all integrations and third-party apps connected to your Slack workspace.
- During audits, assess the necessity and usage of each integration, identifying any unused or redundant apps that can be removed to reduce security risks.
- Review access controls and permissions granted to each app, ensuring they align with the principle of least privilege.
- Access logs monitoring:
- Regularly monitor access logs provided by Slack to track user activity related to integrations and third-party apps.
- Look for any unusual patterns or unauthorized access attempts that may indicate a security breach or misuse of integrations.
- Set up alerts or notifications for suspicious activities to enable timely response and investigation.
- Permission reviews:
- Conduct thorough reviews of the permissions granted to each integration and third-party app within Slack.
- Ensure that the permissions are limited to only what is necessary for the app’s functionality and that excessive permissions are revoked.
- Adjust permissions as needed based on changes in organizational requirements or roles.
- Compliance checks:
- Verify that all integrations and third-party apps comply with relevant regulatory requirements and industry standards.
- Evaluate whether the apps handle sensitive data in accordance with data protection regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS.
- Confirm that the integrations adhere to Slack’s security guidelines and policies.
- Data handling assessment:
- Assess how integrations handle and protect data exchanged within Slack, including messages, files, and other information.
- Ensure that data transmitted to and from integrations is encrypted using secure protocols to prevent unauthorized access.
- Evaluate integrations’ data retention and deletion practices to minimize the risk of data exposure.
- Vendor security assessment:
- Conduct comprehensive security assessments of integration vendors to evaluate their security practices and protocols.
- Review the vendor’s security policies, incident response procedures, and compliance certifications.
- Verify the vendor’s track record and reputation in the industry, including any reported security incidents or breaches.
- Documentation review:
- Maintain detailed documentation of all integrations and third-party apps connected to your Slack workspace.
- Document each integration’s purpose, permissions, security considerations, and compliance status.
- Keep the documentation up-to-date with any changes or updates to integrations or organizational policies.
- Incident response preparedness:
- Develop and regularly update an incident response plan for security incidents involving integrations and third-party apps.
- Define clear procedures for detecting, containing, and mitigating security breaches related to integrations.
- Establish communication channels with integration vendors and relevant stakeholders to coordinate response efforts effectively.
Advanced security tools and resources
UnderDefense provides a comprehensive suite of advanced security services that empower organizations to fortify their security posture, detect and respond to threats effectively, and achieve regulatory compliance.
- Managed Detection and Response (MDR)
- Security Operations Center (SOC)
- Incident Response
- Penetration Testing
- Compliance Assistance
- Vulnerability Management
- Threat Intelligence
- Security Training
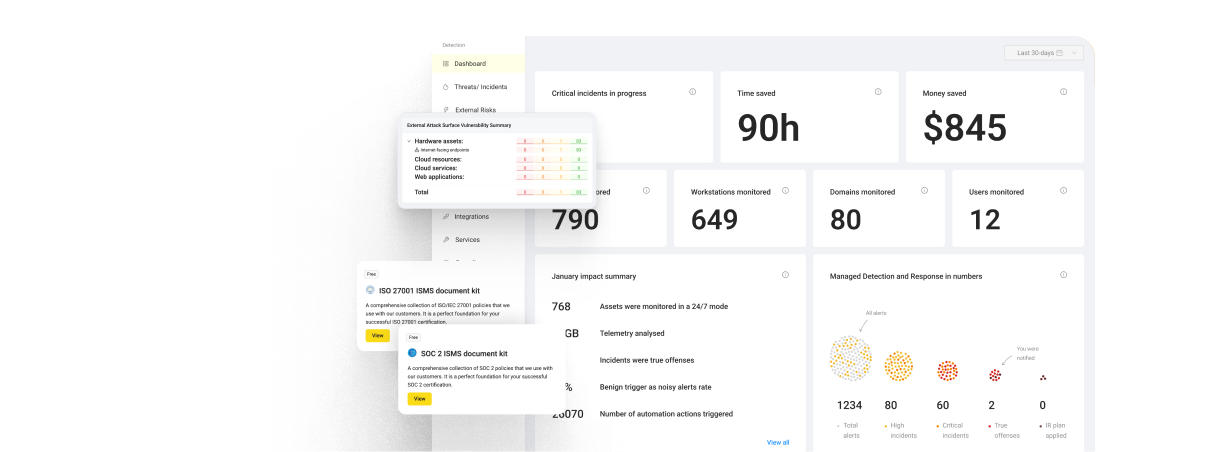
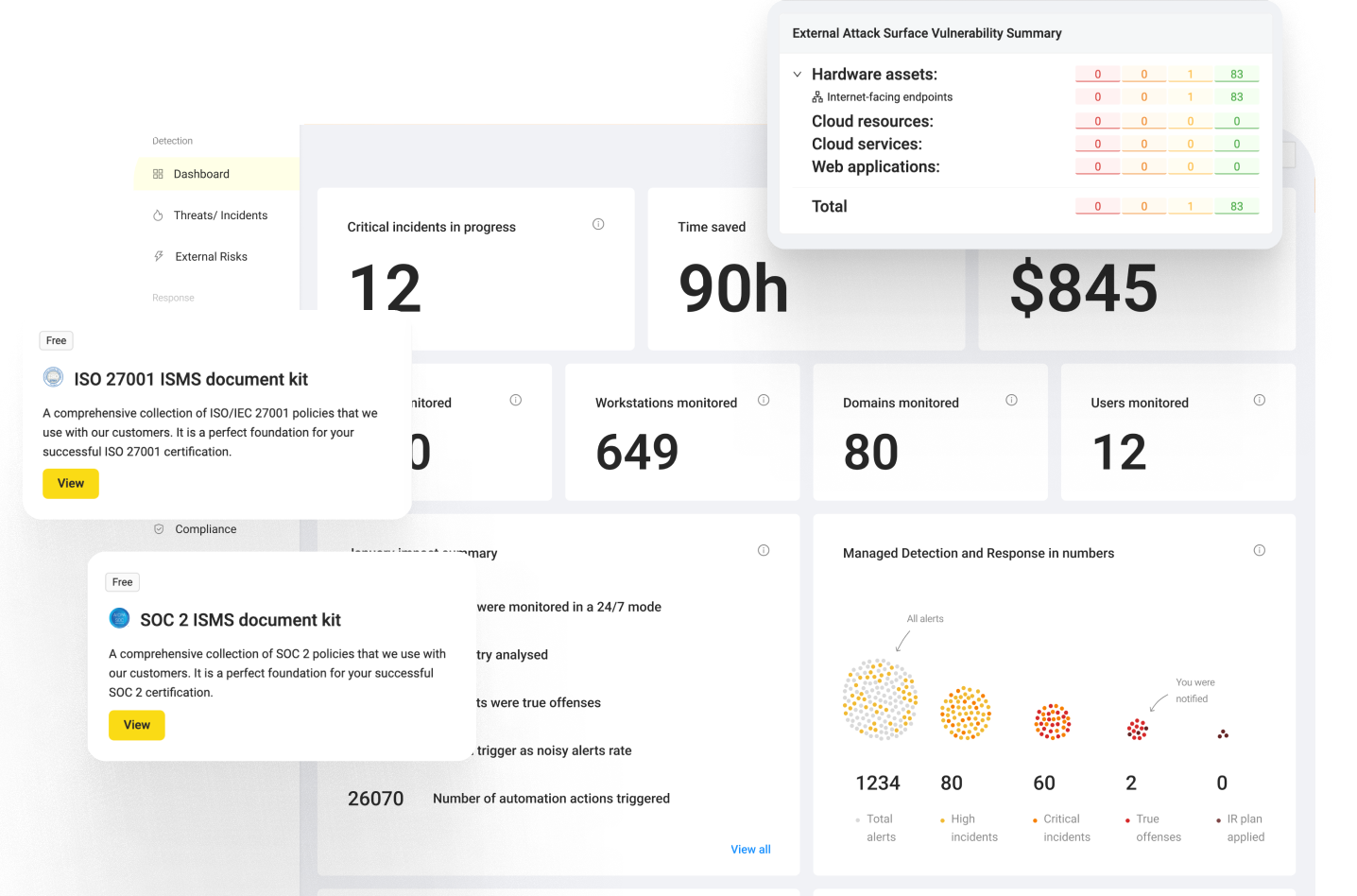
With the integration of the UnderDefense MAXI platform into Slack, organizations can seamlessly access these advanced security capabilities directly within their messaging platform. Features such as MDR, Incident Response, Threat Intelligence, and Compliance Assistance are readily available, enabling streamlined communication and collaboration on security incidents while enhancing overall security resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is Slack more secure than email?
2. Is Slack secure for business?
3. How do I check if my Slack is secure?
To assess the security of your Slack workspace, you can:
- Review and configure security settings, such as enabling 2FA, setting up access controls, and configuring data retention policies.
- Monitor user activity and access logs for suspicious behavior or unauthorized access attempts.
- Conduct security assessments or audits to evaluate compliance with security standards and best practices.
- Regularly update Slack and associated integrations to ensure they’re patched against known vulnerabilities.
- Educate users on security best practices and provide training on recognizing and responding to security threats.
4. What are incident response protocols for a security breach on Slack?
Incident response protocols for a security breach on Slack may include:
- Immediately isolating affected systems or channels to prevent further spread of the breach.
- Investigating the nature and scope of the breach, including how it occurred and what data may have been compromised.
- Notifying relevant stakeholders, including internal teams, Slack support, and potentially affected users.
- Implementing remediation measures, such as patching vulnerabilities, revoking compromised credentials, or resetting permissions.
- Communicating with users and providing guidance on steps they can take to protect themselves.
- Conducting a post-incident review to identify lessons learned and improve security practices for the future.