Table of Contents
- Critical aspects of ISO 27001
- The list of ISO 27001 Policies
- Information Security Policy
- Information Security Policy in Project Management
- Information transfer policy
- Data Classification and Handling Policy
- Data Leakage Prevention Policy
- Risk Management Policy
- Anti-Virus/Anti-Malware Policy
- Web Filtering Policy
- Asset Management Policy
- Password Management Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Access Control Policy
- Physical and Environmental Security Policy
- Working in Secure Areas Policy
- Incident Management Policy
- Threat Intelligence Policy
- Data Retention and Destruction Policy
- Encryption Policy
- Vulnerability Management Policy
- Human Resource Security Policy
- Patch Management Policy
- Software Installation Policy
- Remote Access Policy
- Business-Continuity-Management-Policy
- Supplier and Third-Party Management Policy
- Information Security Policy for the Use of cloud services
- Compliance Policy
- Network Security Policy
- Backup Policy
- Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) Policy
- Log Management Policy
- Removable Media Management Policy
- Change Management Policy
- Document management policy
- Secure development policy
- Data Masking Policy
- Security-Awareness-and-Training-Policy
- Capacity Management Policy
- Internal Audit Policy
- Challenges you may encounter while establishing ISO 27001 policies
- How to address the issues associated with ISO 27001 preparation and speed up the process
- Contact UnderDefense today to become ISO 27001 certified with confidence
ISO 27001 is a globally recognized standard for Information Security Management System (ISMS). It outlines the requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and improving an organization’s ISMS. An ISMS comprises policies, processes, and procedures that help manage information security risks.
ISO 27001 certification allows organizations to showcase to customers and stakeholders that they have taken the necessary measures to protect their information assets and manage security risks effectively.
By obtaining ISO 27001 certification, businesses can demonstrate that their ISMS aligns with the ISO 27001 standard. An accredited certification body grants this certification following a successful audit of the ISMS. It provides independent verification that the company has implemented an ISMS that meets international best practices.
One of the main documents of an ISMS is the information security policy, which defines the scope, objectives, and principles of the ISMS.
Critical aspects of ISO 27001
There are critical aspects that make ISO 27001 a comprehensive and robust framework for information security management:
- Scope and Context: Defining the ISMS scope and identifying the internal and external factors that impact information security.
- Leadership and Commitment: Top management provides administration, commitment, and resources to ensure the effectiveness of the ISMS.
- Risk Assessment and Treatment: Conducting risk assessments to identify threats, vulnerabilities, and potential impacts on information assets. Based on it, they implement appropriate risk treatment measures.
- Information Security Objectives and Planning: Established and developed by an organization, it defines controls, processes, and resources needed for the ISMS.
- Support and Resources: The necessary resources, including competent personnel, infrastructure, and awareness programs, to support the ISMS.
- Implementation and Operation: Implementing and operating controls and processes to manage information security risks effectively. It includes asset management, access control, cryptography, incident management, and business continuity.
- Performance Evaluation: Organizations monitor, measure, analyze, and evaluate the performance of the ISMS to ensure its effectiveness. It involves conducting internal audits, management reviews, and addressing non-conformities.
- Continual Improvement: Boosting the effectiveness of the ISMS through corrective actions, preventive actions, and lessons learned from incidents and reviews.
The list of ISO 27001 policies
UnderDefense services include access to an ISO 27001 information security policy templates kit, which serves as a foundation for establishing the necessary policies and controls within your ISMS. Our ISO 27001 information security policy templates toolkit covers different areas such as IT, HR, office/physical security, and surveillance. Additionally, we guide how to effectively complete and customize our ISO 27001 ISMS templates to meet your specific organizational needs.
Here is an overview of the policies typically included in an ISO 27001 framework that serves as a foundation for information security practices:
 Information Security Policy |  Patch Management Policy |
 Information Security Policy in Project Management |  Software Installation Policy |
 Information Transfer Policy |  Remote Access Policy |
 Data Classification and Handling Policy |  Business Continuity Management Policy |
 Data Leakage Prevention Policy |  Supplier and Third-Party Management Policy |
 Risk Management Policy |  Information Security Policy for the Use of cloud services |
 Anti-Virus/Anti-Malware Policy |  Compliance Policy |
 Web Filtering Policy |  Network Security Policy |
 Asset Management Policy |  Backup Policy |
 Password Management Policy |  Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) Policy |
 Acceptable Use Policy |  Log Management Policy |
 Access Control Policy |  Removable Media Management Policy |
 Physical and Environmental Security Policy |  Change Management Policy |
 Working in Secure Areas Policy |  Document management policy |
 Incident Management Policy |  Secure development policy |
 Threat Intelligence Policy |  Data Masking Policy |
 Data Retention and Destruction Policy |  Security Awareness and Training Policy |
 Encryption Policy |  Capacity Management Policy |
 Vulnerability Management Policy |  Internal Audit Policy |
 Human Resource Security Policy |
1. Information Security Policy
Sets goals for protecting information assets and provides a framework for implementing controls.
2. Information Security Policy in Project Management
Addresses security considerations, defining responsibilities, requirements, and protocols for handling sensitive information during projects.
3. Information Transfer Policy
Sets guidelines and procedures for securely transferring information. It considers the sensitivity, confidentiality, and criticality of data during transit and ensures that sensitive information is appropriately categorized, handled, and securely transferred.
4. Data Classification and Handling Policy
Defines how an organization categorizes and handles different data based on sensitivity, confidentiality, and criticality.
5. Data Leakage Prevention Policy
This policy includes encryption, access controls, and monitoring to detect and prevent unauthorized data disclosure, leakage, or accidental loss. It helps to enforce data security measures and promotes compliance with relevant regulations and privacy requirements.
6. Risk Management Policy
Outlines the process for identifying, assessing, and managing information security risks. It also includes procedures for risk assessment, risk treatment options, and the acceptance of residual risks.
7. Anti-Virus/Anti-Malware Policy
Outlines the requirements and best practices for protecting an organization’s information systems and networks from viruses and malicious software.
8. Web Filtering Policy
By integrating it into their security framework, alongside the Anti-Virus/Anti-Malware Policy, the organizations enhance their overall defense against malware or other risky web content.
9. Asset Management Policy
Outlines how a company manages its assets throughout its lifecycle.
10. Password Management Policy
A set of guidelines and procedures that govern the creation, use, and protection of passwords within an organization.
11. Acceptable Use Policy
Defines acceptable and prohibited uses of information technology resources. It outlines the expected behavior and responsibilities of individuals with access to these resources, including employees, contractors, and other authorized users.
12. Access Control Policy
Defines the rules and procedures for granting access to information and information processing facilities. It covers user access management, authentication mechanisms, and access control for systems and networks.
13. Physical and Environmental Security Policy
Addresses the necessary physical security measures to safeguard information assets and processing facilities. It covers secure areas, equipment protection, secure disposal, and clear desk and screen policies.
14. Working in Secure Areas Policy
Provides specific guidelines and procedures for employees operating within designated secure areas. It ensures that access to these areas is properly controlled, outlines measures to protect equipment and assets, establishes protocols for the secure disposal of sensitive information, and enforces clear desk and screen policies and practices.
15. Incident Management Policy
Establishes procedures for reporting, responding to, and managing security incidents. It outlines roles, incident classification, and escalation processes.
16. Threat Intelligence Policy
Established to gather and analyze threat information, enhancing incident response and proactive security measures.
17. Data Retention and Destruction Policy
Defines how an organization retains, stores, and ultimately destroys data securely and competently.
18. Encryption Policy
Governs the usage of encryption technologies to protect sensitive information and ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
19. Vulnerability Management Policy
Governs the identification, assessment, remediation, and monitoring of vulnerabilities within a company’s IT infrastructure and systems.
20. Human Resource Security Policy
A set of guidelines and procedures that outline the business’s expectations and requirements for managing the security of human resources and protecting sensitive information related to employees, including hiring, onboarding, off-boarding, and transfer processes.
21. Patch Management Policy
Governs the management and deployment of software patches and updates.
22. Software Installation Policy
Governs installation, management, and software use.
23. Remote Access Policy
A set of guidelines and procedures that govern secure and authorized remote access to an organization’s network, systems, and resources.
24. Business Continuity Management Policy
Outlines the organization’s approach to ensure that critical information and IT resources are available during and after a disruption. It includes procedures for backup, disaster recovery, and business continuity planning and testing.
25. Supplier and Third-Party Management Policy
Defines the requirements and procedures for managing relationships with suppliers and third parties with access to the company’s information assets. It covers due diligence, contracts, monitoring, and auditing of suppliers.
26. Information Security Policy for the Use of cloud services
Extends the principles of the Supplier and Third-Party Management Policy to cover cloud service providers. It outlines the requirements and procedures for their evaluating, contracting, monitoring, and auditing.
27. Compliance Policy
Ensures that an organization complies with applicable laws, regulations, and contractual requirements related to information security. It includes procedures for legal and regulatory compliance, privacy protection, and data protection.
28. Network Security Policy
A set of guidelines and procedures defining the rules and measures for protecting network infrastructure and ensuring network resources’ confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
29. Backup Policy
A set of guidelines and procedures that outline how an organization performs data backups, ensures data recoverability and protects against data loss.
30. Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) Policy
A set of guidelines that govern the use of personal devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops, for work-related purposes.
31. Log Management Policy
A set of guidelines and procedures that govern the collection, storage, analysis, and retention of log data generated by various systems, applications, and network devices.
32. Removable Media Management Policy
Governs the transfer and handling of physical media (such as hard drives, USB drives, DVDs, or paper documents).
33. Change Management Policy
Governs how changes are planned, implemented, and controlled within an organization’s IT infrastructure and systems.
34. Document management policy
Governs the creation, control, distribution, storage, retention, and disposal of documented information within an Information Security Management System (ISMS) or organization.
35. Secure development policy
Governs safe development practices. It encompasses security principles integrated throughout the entire software development lifecycle to minimize vulnerabilities and protect against potential threats.
36. Data Masking Policy
Defines procedures for implementing data masking techniques to safeguard sensitive data during development and testing processes. It outlines substituting sensitive information with realistic but fictitious data to reduce the risk of unauthorized access or exposure.
37. Security Awareness and Training Policy
Outlines the organization’s approach to promoting security awareness among employees and ensuring they receive appropriate training to mitigate risks. The policy emphasizes the importance of fostering a security-conscious culture and provides guidelines for implementing security awareness programs and training initiatives.
38. Capacity Management Policy
Outlines the effective management and optimization of IT resources and infrastructure to meet current and future demands. This policy ensures that the organization’s IT systems, networks, and services have adequate capacity to support business operations and deliver optimal performance.
39. Internal Audit Policy
Defines the framework, objectives, and responsibilities for conducting internal audits. This policy establishes the purpose and scope of internal audits, guiding the systematic and independent evaluation of processes, controls, and compliance with policies and regulations.
Challenges you may encounter while establishing ISO 27001 policies
- Lack of Awareness: A significant obstacle is the limited knowledge of the ISO 27001 standard and its requirements. This lack of understanding can hinder the process of obtaining support from stakeholders and securing their commitment to implementing the policies.
- Resource Constraints: Establishing ISO 27001 policies requires dedicated resources, including personnel, time, and financial investment. Limited resources can hinder the development and implementation process, causing delays or compromises in the effectiveness of the policies.
- Complexity and Scope: The ISO 27001 standard is comprehensive and covers various aspects of information security management. The complexity and scope of the standard can be overwhelming, especially for organizations without prior experience or expertise in information security.
- Organizational Culture: Implementing ISO 27001 policies often requires a cultural shift towards a security-conscious mindset. Resistance to change or a lack of emphasis on information security can pose challenges in ensuring compliance and adherence to the policies.
- Risk Assessment and Treatment: ISO 27001 emphasizes the importance of conducting a thorough risk assessment and implementing risk treatment measures. Organizations may struggle to identify and assess information security risks and determine appropriate risk treatment actions.
- Policy Customization: While ISO 27001 provides a framework, policies must be tailored to each company’s needs and context. Developing policies that align with organizational objectives and meet the standard requirements can be challenging, especially when trying to strike a balance between security and operational efficiency. Utilizing ISO 27001 policy templates can serve as a starting point, providing a foundation that can be customized to address unique requirements and considerations.
- Documentation and Documentation Control: ISO 27001 requires extensive documentation, including policies, procedures, and records. Maintaining proper documentation control, ensuring accuracy, version control, and accessibility of documents can be a significant challenge, especially as the organization grows and evolves. To facilitate this process, organizations can leverage ISO 27001 documentation templates that provide a structured and standardized approach to developing policies, procedures, and other necessary documents.
- Training and Awareness: Effective implementation of ISO 27001 policies requires adequate employee training and awareness programs. Ensuring that employees understand their roles, responsibilities, and the importance of information security, can be a challenge, particularly in large or geographically dispersed organizations.
- Compliance and Audit Readiness: Compliance with ISO 27001 policies and preparing for internal or external audits can be demanding. Maintaining ongoing compliance, addressing non-conformities, and continuously improving the ISMS can require significant effort and attention to detail.
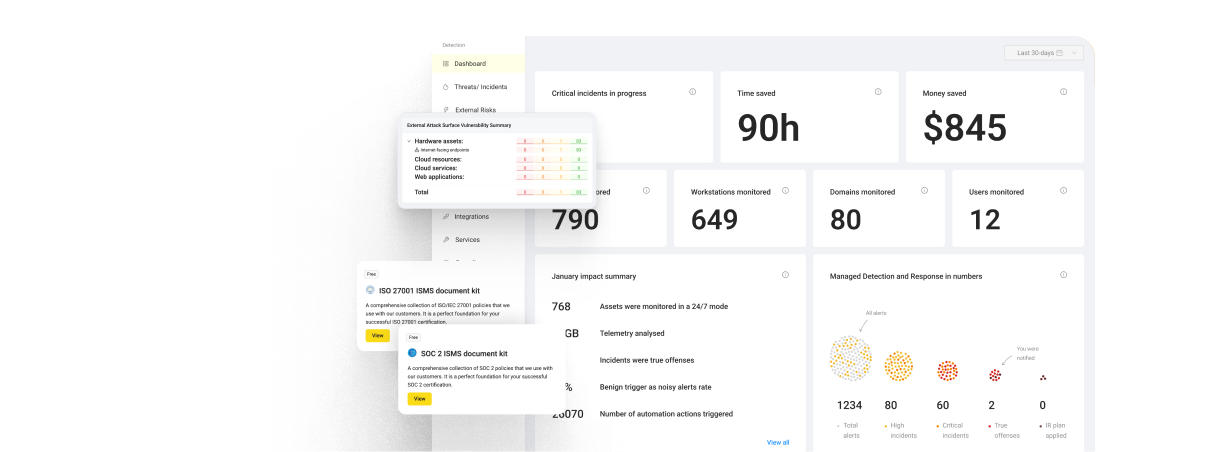
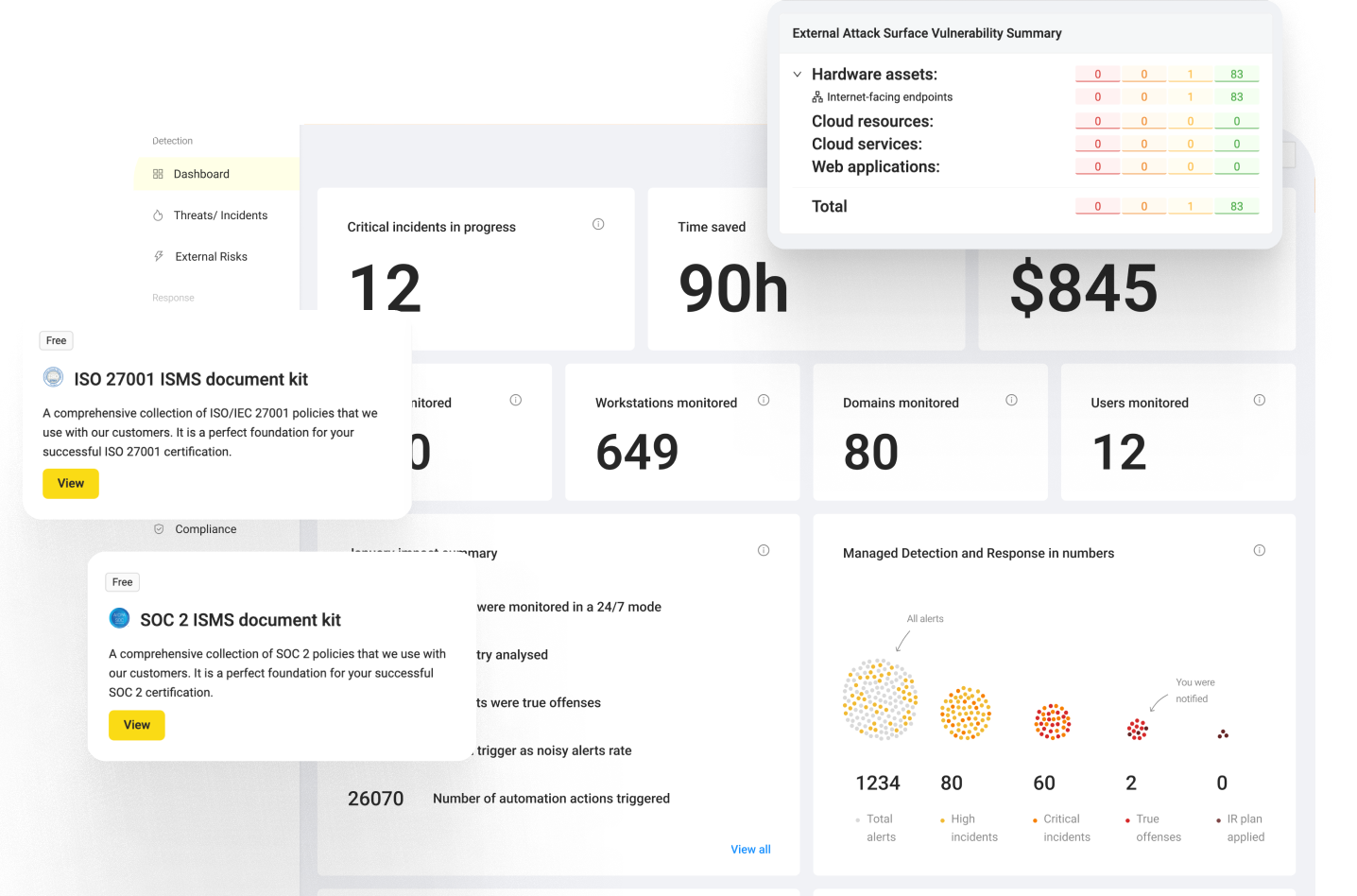
Access UnderDefense ISO 27001 Policy Templates to Streamline Your Certification Journey
The ISO 27001 internal audit plays a vital role in monitoring the effectiveness of the ISMS and ensuring compliance with the standard. It helps organizations identify and address gaps in their information security practices, mitigating risks and enhancing overall security posture.
Conducting an ISO 27001 internal audit requires competence in auditing principles, ISO 27001 requirements, and information security management. It may be beneficial to seek external assistance from experts to ensure a thorough and unbiased process.
UnderDefense provides free policy templates that offer standardized frameworks for creating essential information security policies and procedures aligned with ISO 27001 requirements. By utilizing these pre-designed templates, you can save time and effort, simplifying the certification process.
Whether you are confident in your skills or prefer an independent approach, request the ISO 27001 Certification Policy Templates on our website to kickstart your certification process today.
Save up to $7000 and a month’s worth of time!
Use these templates to decrease the additional costs of ISO 27001 certification
How to address the issues associated with ISO 27001 preparation and speed up the process
Creating comprehensive and effective ISO 27001 ISMS templates can be challenging for organizations. You may need to rely on industry experts for free ISO 27001 information security policy templates and support to save time and costs and make your policies clear, consistent, and goal-oriented.
UnderDefense offers a free set of ISO 27001 ISMS templates with best practices. We can also help you with the entire process of making, using, and mapping your security policies for ISO 27001 compliance. Our ISO 27001 information security policy template kit is a great resource that many customers have used.
To enhance your organization’s information security management with ISO 27001, start implementing these actions now:
- Increase Awareness and Education: Invest in raising awareness and providing education on the ISO 27001 standard and its benefits. Conduct training sessions, workshops, or information sessions to familiarize stakeholders with the requirements and the importance of information security management.
- Seek External Expertise: Consider engaging external consultants or experts with experience in ISO 27001 implementation. They can provide guidance and help accelerate the implementation process by leveraging their expertise and knowledge. Additionally, organizations may find value in utilizing ISO 27001 documentation templates, which can serve as helpful resources in developing their information security policies and procedures.
- Customize Policies: Tailor the ISO 27001 policies to your organization’s specific needs and context. Avoid unnecessary complexity and ensure the policies align with the organization’s objectives while meeting the standard requirements. Regularly review and update policies, conduct internal audits, and address any non-conformities or improvement opportunities identified.
Being prudent makes all the difference
Contact UnderDefense today to become ISO 27001 certified with confidence
If you possess the necessary expertise and confidence to proceed independently, our UnderDefense MAXI platform offers a free download of ISO 27001 Certification Policy Templates that can serve as your guiding light. Request the templates now and dive into the certification process with certainty.
However, we understand that the road to certification can be complex, and there may be time constraints or concerns about achieving the desired outcome. That’s where UnderDefense is eager to help you secure your ISO 27001 certification. Our commitment to your success goes beyond providing templates. We offer a “reserve” of knowledge, drawing upon our experience and expertise to ensure you pass the certification on your first attempt.
Here’s how we can assist you in becoming ISO 27001 compliant:
- Evaluate your current state of readiness and identify any gaps that need to be addressed
- Develop a complete roadmap using our ISO 27001 Downloadable Audit Checklist
- Enhance your assessment process with our ISO 27001 Internal Audit Checklist
- Customize the ISO 27001 policies to align with your unique business requirements while ensuring compliance
- Provide expert vCISOs who will offer invaluable guidance and support throughout every stage of the certification process, alleviate stress, save time, and reduce costs associated with ISO 27001 certification
- Conduct a Penetration Test if you have not done it yet to identify vulnerabilities and fortify your defenses
- Conduct Security Awareness Training to empower your staff with the knowledge and best practices necessary for maintaining a secure environment
- Streamline all processes with our compliance services
Are you ready to take your organization’s security posture to the next level with ISO 27001 certification? Contact our sales today for invaluable advice and guidance on your certification journey.