Today, cybersecurity and resilience are the major challenges for businesses. So, it is no surprise that these items top the agenda of nearly all meetings in most industries. Combined with the rapid cloud adoption, they require a deep understanding of risks you may face and the ways how to ensure business continuity when an attack happens.
You have the right to know
In this guide, we will share three essential steps for you to take to strengthen the cyber resilience of AWS cloud environments. We will cover everything starting from native tools and proceeding with suggested services to help you build multilayered protection and necessary open-source libraries. Additionally, we will discuss why cloud security fails and how you, as a CIO or CISO, can prevent that.
Let’s start from the basics by finding out what cyber resilience is.
What is cyber resilience?
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) defines cyber resilience (CR) as “the ability to anticipate, withstand, recover from, and adapt to adverse conditions, stresses, attacks, or compromises on systems that include cyber resources”.
Also, NIST developed a major guidance on cyber resilience, namely “Developing Cyber-Resilient Systems: A Systems Security Engineering Approach” (SP 800-160 Vol. 2, Rev. 1), which provides comprehensive knowledge on the subject.
Now, let’s dive into the topic, starting with the CR framework, which consists of the elements called “constructs,” including:
- Goals (anticipate, withstand, recover, and adapt): These goals are the link that connects decisions on the system, business process, and organization levels. CR is important on multiple levels within your organization. Its goals support the connection between the elements of risk management.
- Objectives: It is one of the main elements that affect the whole CR framework. You need to understand what the business needs in terms of resilience of your application. The objectives should be precisely concrete to build a really strong and working CR framework.
There are two key metrics: recovery point objective (RPO) and recovery time objective (RTO). RPO refers to how much data you can potentially lose, for example, one hour’s worth of data or five minutes’ worth of data. RTO defines how long your systems can be down before your business suffers significant damage (financial, reputational, etc.).
- Techniques are strongly dictated by the chosen goals and objectives. In other words, techniques reflect how you can achieve CR in your organization. NIST provides the description of 14 techniques, each with its capabilities, intended results, or the processes it requires.
It’s also important to understand what kind of threats you might be facing. It’s advised to use only a selective set of techniques to make certain improvements and change them over time after new threats or technologies or a new strategy appear.
- Approaches are part of technologies and processes used in techniques and are defined by how the capabilities are implemented or how the intended results are achieved.
- Design principles suggested by NIST as guidance for CR system engineers and architects. They can be applied in different ways and at different stages in the system life cycle.
Strategic CR design principles are made to guide engineers and analysts about the necessary changes and align them with the current business objectives. Structural design principles describe specific CR recommendations you need to make about your system.

All CR constructs are interconnected and co-dependable, so when you’re building a strategy, it’s essential to understand how it works as a whole and follow NIST recommendations.
Every element of the CR framework is related to risk management as a defining point. As mentioned before, you need to prioritize your business goals and objectives at that moment and then move to choosing suitable techniques, approaches, and design principles. Your engineers should analyze every step and its effect on the organization’s CR to ensure it was successfully chosen and implemented.
Next, we will look into the main reasons why cloud security fails and outline CR measures we recommend implementing to protect business.
Why cyber resilience is now vital for all organizations
JupiterOne revealed a shocking 589% growth in cloud attack surface. It indicates a snowball effect: the number of cyber assets doubled in 2023 compared to the previous year. Consequently, it’s not only a proportional increase in security vulnerabilities. It also includes previously unresolved ones. With that said, you should act now to prepare your cloud environments for future attacks.

The challenges of recent years have put additional pressure on the business sector. Companies are forced to deal with unexpected disruptions and continue the remote work practice, leading to more rapid adoption of cloud technologies. Such an approach increased the demand for designing a more actionable CR plan, which:
- Mitigates financial losses and reduces fines and penalties
- Grows client loyalty and brand reputation
- Increases competitive advantage in the market
- Lowers the risks of breaches and security incidents
Cyber resilience comes into play when it’s clearly understandable that an attack has happened, and it’s critical to preserve your organization’s IT infrastructure, network, data, and applications, adapt to the situation, and resume functioning. By accepting the reality of being compromised, your next step is to execute “a plan B” that should allow you to regain control where you can, move resources to a new location, and activate a potent approach to keep business on track.
Why cloud security fails
Traditional cybersecurity tools do not provide holistic protection for cloud environments, exposing your organization to unnecessary risks. Sysdig discovered that about 75% of companies use cloud services with high or critical vulnerabilities. Those security gaps can be addressed with the appropriate tools, but most importantly, you can mitigate them by creating a reliable CR framework.

But let’s start with the basics and check the following points:
- It’s better not to put several security roles on one person because it will lead to failure.
- SecOps and DevOps cover different areas.
- Security isn’t equal to detection. You must be ready to respond and know what to do when an attack happens.
- Simulation is essential. Be ready for a lot of planning, modeling, and becoming multi-cloud if needed.
- The bigger your infrastructure or deployment becomes, the higher the risk and the bigger the disconnection between various parts of the organizational structure.
- Cloud detection and response is a 24/7 job, and you must get it done to stay protected.
It’s understandable that you can’t eliminate risks, but you surely can manage them. Considering the most common challenges that we put above is the beginning of building the cyber resilience of your AWS cloud.
Now let’s find out what steps you should take to improve your cloud security resilience and protect digital assets, applications, and data.
STEP 1. Activate Amazon cloud-native services
The cloud requires a different approach to security measures and cyber resilience, promoting the use of native services. Cloud has restricted access for third parties, including security vendors, to protect data at a maximum level. Security tools you see in the market can collect and consolidate responses from cloud-native services about attacks or potential threats.
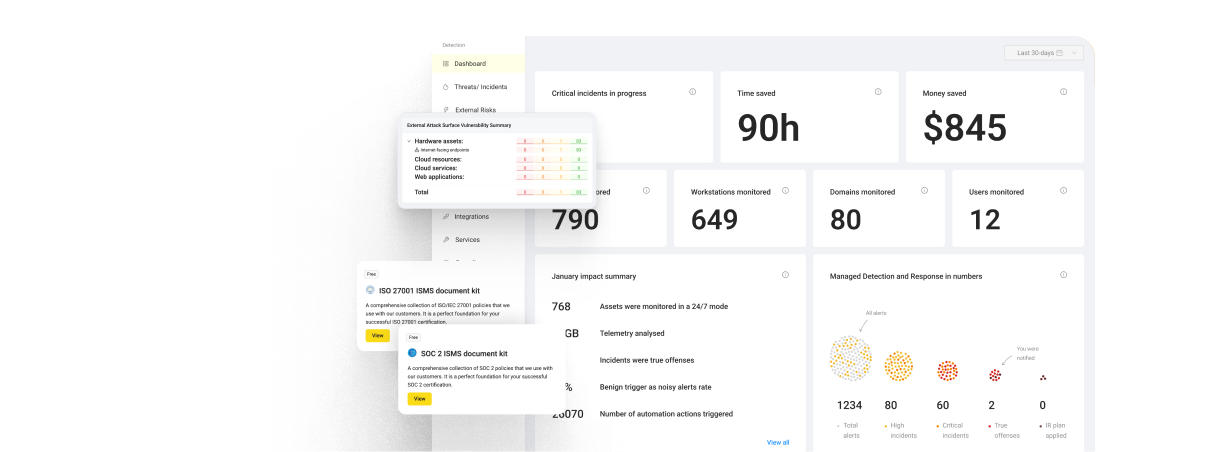
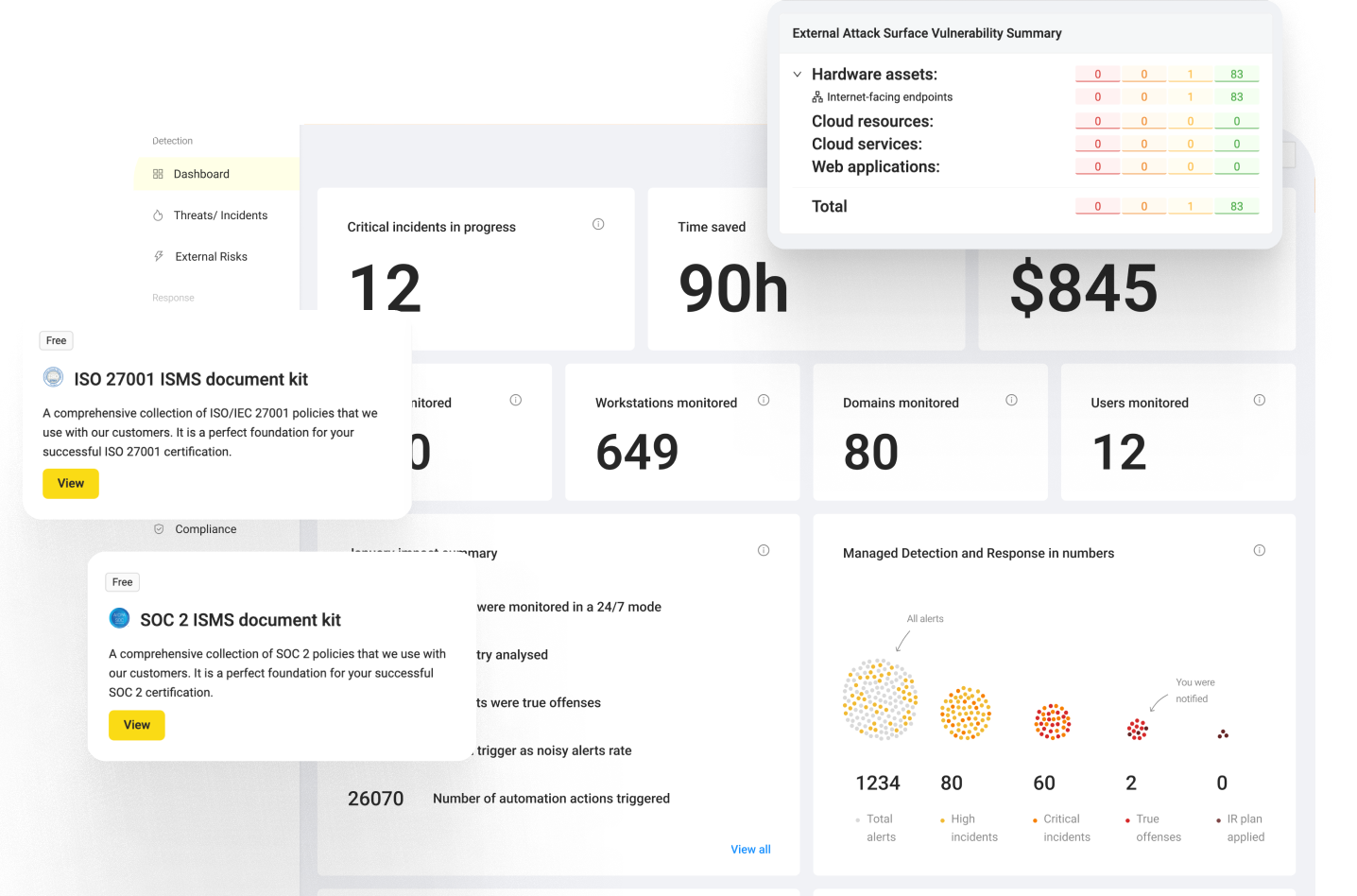
In the scheme below, you can see how the Resilience Hub orchestrates all services to strengthen your AWS cloud cyber resilience posture:

We want to emphasize that if you want to set resilience goals for your AWS cloud, assess your security posture, and improve it, then you must use cloud-native solutions as one framework to achieve those goals.
STEP 2. Boost AWS tools performance with UnderDefense MAXI
The UnderDefense MAXI platform offers a new approach to cloud security. The main purpose of it is to ensure 24/7 threat detection, response automation, compliance, and vulnerability management. Additionally, you can integrate AWS cloud to not only orchestrate the work of various solutions but also improve the performance of cloud-native services.
Here are the top five UnderDefense MAXI security features you can utilize for AWS cloud:
- Alert-to-triage takes 2 minutes, while with native AWS solutions it takes 18 minutes.
- ML-powered threat detection feature empowers AWS GuardDuty.
- The vulnerability detection feature supplements AWS Inspector.
- Data exposure detection streamlines the work of the AWS IAM Access Analyzer.
- Prowler, an open-source security library, helps with the Center for Internet Security (CIS) AWS Foundations Benchmark.
In other words, UnderDefense MAXI uses AWS cloud-native services under the hood, allowing you to consolidate and analyze received alerts in one place. The platform acts as another security layer for your systems. It’s also worth clarifying that you need to be active according to AWS services on your side and integrate them into the MAXI platform to make it work.

STEP 3. Apply MITRE framework
Previously, we’ve explored how effective cybersecurity requires several layers of defense, which function smoothly to provide comprehensive protection against cyber threats. Besides deploying costly tools that ensure these layers, engineers must also have a solid knowledge of adversaries’ tools and techniques and available approaches to protect your organization. MITRE has built comprehensive databases open to the public to address the continuously evolving threats.
Here’s the MITRE framework we recommend checking and following:
- ATT&AC: a knowledge base of adversary tactics and techniques you must prepare for. It also provides procedure examples with detailed explanations.
- Engage: a framework for defenders to safely and effectively engage in denial, deception, and adversary engagement.
- D3FEND: a knowledge base of cybersecurity countermeasures divided by models.
- CALDERA: a framework for automated adversary emulation, which means testing your network for resilience against advanced threats.
- Cyber Resiliency Engineering Framework (CREF) Navigator: this visualization tool has goals, objectives, techniques, and approaches aligned with NIST recommendations and offers corresponding solutions by MITRE.
“Resiliency is the ultimate goal of cybersecurity,” said Wen Masters, VP of cyber technologies at MITRE. By using these guides with useful tables and well-explained concepts, you can apply recommendations and easily prioritize your CR goals.

Final advice on cyber resilience of AWS cloud
Keeping AWS cyber resilience on top of its performance is a continuous task. We have already gone through the essential steps you need to take to protect your business from disruptions. Just building multiple layers of security and leaving it without regular revisions can put you at risk. There are several essential questions you need to ask your DevOps or IT experts:
- What is the delay in time to detect in your AWS environment(s)?
- Do you have immutable backups and infrastructure as a code to recover quickly?
- How fast could you get online in the worst-case scenario?
- When was the last time you tested it?
- What are your most frequent threats, and how would you know if your system gets hacked?
Depending on what kind of answers you get, it will indicate if your CR strategy works correctly or needs urgent improvements. In 2023, Pluralsight stated that about 70%of organizations have more than half of their infrastructure in the cloud. Such rapid adoption requires a reliable security framework. You must always be prepared to detect and recover from a threat with minimum losses.

Here are a few things you need to do to stay prepared:
- Use DevOps and SecOps practices to prepare regular security reviewing, hardening, and fine-tuning.
- Deploy 24/7 threat detection and response tools or buy a SOC-as-a-service from a reputed vendor.
- Perform professional AWS hacking exercises for visibility testing.
- Conduct recoverability testing regularly.
Following these steps, you can keep your finger on the pulse of your security status and cover the gaps as soon as they appear.
Being prudent makes all the difference
Final thoughts
As organizations increasingly migrate to the cloud, ensuring cyber resilience in AWS cloud has become crucial. By implementing a layered approach that includes activating cloud-native security features, leveraging the UnderDefense MAXI platform, and applying the MITRE framework, you can effectively safeguard your data, applications, and infrastructure from potential cyber threats.
If you need a reputed vendor to help you apply this holistic approach that will enhance your organization’s security posture, then UnderDefense is the right choice. Our experts can guide you through each step of improving AWS cloud security, find suitable solutions, and seamlessly integrate them with UnderDefense MAXI. Contact us today to protect your business tomorrow.
Disclaimer: The text of the article is based on the security webinar presented by Nazar Tymoshyk, CEO at UnderDefense, Art Ocain, CISO at Airiam, and Vasyl Herman, AWS DevOps Engineer at UnderDefense.